HOME
JC Age-friendly City Project - p2_academic_output
Age-friendly Community and the Decade of Healthy Ageing
Academic Output
Journals
Chui, H.K, Lu, S., Guo, Y., Chan, O.F., C., Cheung, C.S., Guo, Y., Liu, Y., Chan, S. W., Tang, W.M., Au, A., Wen, Z., Yu, R., Bai, X., Mok, K.H., Woo, J., & Lum, T. Y. (2022). Changes in older adults' perceptions of age-friendliness in Hong Kong: A three-year mixed-methods study. Cities, 127, 103748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2022.103748
Lai, E. T., Yu, R., & Woo, J. (2021). Social gradient of self-rated health in older people—the moderating/mediating role of sense of community. Age and Ageing, 50(4), 1283-1289. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afaa277
Woo, J., Leung, D., Yu, R. Lee, R. & Wong, H. (2021). Factors Affecting Trends in Societal Indicators of Ageing Well in Hong Kong: Policies, Politics and Pandemics. The Journal of Nutrition, Health & Aging, 25(3), 325-329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-020-1488-z
Woo, J., Yu, R., Cheung, K., & Lai, E.T.C. (2020). How Much Money Is Enough? Poverty and Health in Older People. The Journal of Nutrition, Health & Aging, 24(10), 1111-1115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-020-1444-y
Fang, Y., Chau, A. K. C., Fung, H. H., & Woo, J. (2019). Loneliness shapes the relationship between information and communications technology use and psychological adjustment among older adults. Gerontology, 65(2), 198-206. https://doi.org/10.1159/000495461
Yu, R., Wong, M. & Woo, J. (2019). Perceptions of neighborhood environment, sense of community, and self-rated health: An age-friendly city project in Hong Kong. Journal of Urban Health, 96(2), 276-288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11524-018-00331-3
Sun, Y., Phillips, D. R., & Wong, M. (2018). A study of housing typology and perceived age-friendliness in an established Hong Kong new town: A person-environment perspective. Geoforum, 88, 17-27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoforum.2017.11.001
Sun, Y., Chao, T.Y., Woo, J., & Au, D.W.H. (2017). An institutional perspective of "Glocalization" in two Asian tigers: The "Structure-Agent-Strategy" of building an age-friendly city. Habitat International, 59, 101–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2016.11.013
Wong, M., Yu, R. & Woo, J. (2017). Effects of perceived neighbourhood environments on self-rated health among community-dwelling older Chinese. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(6), 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14060614
Wong, A., Chau, A. K. C., Fang, Y., & Woo, J. (2017). Illuminating the psychological experience of elderly loneliness from a societal perspective: A qualitative study of alienation between older people and society. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(7), 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14070824
Fang, Y., Chau, A. K. C., Wong, A., Fung, H. H., & Woo, J. (2017). Information and communicative technology use enhances psychological well-being of older adults: The roles of age, social connectedness, and frailty status. Aging & Mental Health, 22(11), 1516-1524. https://doi.org/10.1080/13607863.2017.1358354
Woo, J., Yu, R., Leung, J., Wong, M., Lau, K., Ho, H.C., Yip, H.M., Kwok, J., Lai, D., Tsien, T. & Au, A. (2017). Urban characteristics influencing health of older people: What matters. International Journal of Innovative Research in Medical Science, 2(12): 1561-1568. https://doi.org/10.23958/ijirms/vol02-i12/01
Book Chapters
Woo, J., Cheung, K., & Chau, A., (2023). Strategies for creating an age-friendly city: Hong Kong as a case study. Hong Kong: The CUHK Jockey Club Institute of Ageing. PDF
Sun, Y., Chao, T. Y. S., Au, D. W., Yung, E. H., & Woo, J. (2022). The age-friendly movement in an Asian context. In Christie M. Gardiner & Eileen O'Brien Webb (Eds.), The Age-friendly lens (pp. 89-103). London: Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003038658
Phillips, D. R., Woo, J., Cheung, F., Wong, M., & Chau, P. H. (2018). Exploring the age-friendliness of Hong Kong: Opportunities, initiatives and challenges in an ageing Asian city. In T. Buffel, S. Handler, & C. Phillipson (Eds.), Age-Friendly cities and communities: A global perspective. Bristol: Policy Press Scholarship Online. https://doi.org/10.1332/policypress/9781447331315.003.0007
Sun, Y., Wong, A., Chau, A. K. C., Wong, M. & Woo, J. (2017). Listening to the Elders: The Case of a Bottom-Up, Context-Sensitive Place Audit in Tai Po District of Hong Kong. In T.Y.S. Chao (Ed.), Planning for greying cities: Age-friendly city planning and design research and practice (pp.72-88). New York: Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315442884
Conference Proceedings
Fang, Y., Chau, A. K. C., Fung, H. H., & Woo, J. (2019). Loneliness shapes the relationship between ICT use and psychological adjustment among older adults [Oral presentation]. The GSA 2019 Annual Scientific Meeting, Austin, U.S.A. https://doi.org/10.1093/geroni/igz038.1950
Chau, A. K. C., Wong, A., Fang, Y., & Woo, J. (2018). Demographic, health, social and environmental correlates of loneliness in Hong Kong older adults [Oral presentation] The U.S.-Hong Kong 2018 Conference: Aging across Time and Contexts, Hong Kong, China.
Chau, A. K. C., Fang, Y., Wong, A., Yu, R., & Woo, J. (2017). Social connections mediate the association between frailty and meaning in life in older people [Poster presentation]. The 21st IAGG World Congress of Gerontology and Geriatrics on "Global Aging and Health: Bridging Science, Policy, and Practice", San Francisco, USA. https://doi.org/10.1093/geroni/igx004.2027
Yu, R., Woo, J., Lum, T., Lou, V., Ma, C., Kwan, M., Au, A. & Lai ,D.W. (2017). Building Hong Kong into an Age-friendly city: Results from a baseline assessment [Poster presentation]. The 21st IAGG World Congress of Gerontology and Geriatrics on "Global Aging and Health: Bridging Science, Policy, and Practice", San Francisco, USA. https://doi.org/10.1093/geroni/igx004.3985
Yu, R., Wong, M., Chow, J., Miao, H.Y. & Woo, J. (2016). Association between perceived social environment and sense of community in older Chinese people in Hong Kong [Poster presentation]. The JCSPHPC 15th Anniversary International Conference on "Innovations in Public Health Sciences", Hong Kong, China.
JC Community eHealth Care Project - p4_resources_sub03
JC Community eHealth Care Project
Useful links
JC Community eHealth Care Project - p4_resources_sub01
JC Community eHealth Care Project
Multi-component Intervention

hotweather_main
Introduction
Hot Weather Conditions in Hong Kong
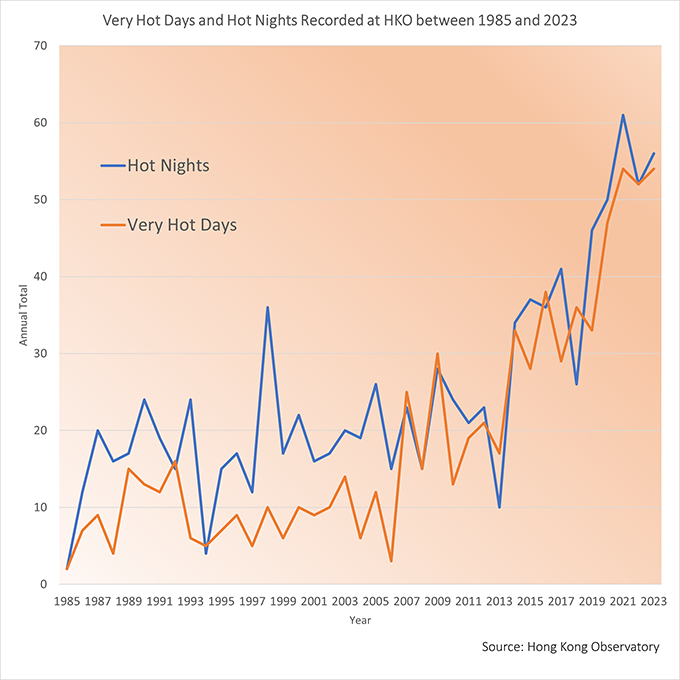
Hong Kong, like the rest of the world, has experienced a warming trend over the past century or so, with an increase in the number of hot nights1 and very hot days2 and a decrease in the number of cold days3. Since 2021, the Hong Kong Observatory has recorded an average of more than 50 very hot weather days per year, the highest number since records began. Extremely hot weather4 is expected to become more frequent in the future.
1 Hot Nights: days with a minimum temperature of 28°C or above
2 Very Hot Days: days with a maximum temperature of 33°C or above
3 Cold Days: days with a minimum temperature of 12°C or below
4 Extremely Hot Weather: days with a maximum temperature of 35°C or above
The Institute initiated its research and district work in 2020. In collaboration with local organisations, it conducted educational programmes on the impact of extreme weather on the elderly and the general public. Furthermore, community-based strategies were developed to address the challenges posed by extreme weather.

Health Risks of the Elderly in Hot Weather
As the years go by, the body functions of the elderly change. This results in slower behavioural responses and a reduction in sensitivity to thirst and temperature. This makes it challenging for the elderly to cope with hot weather effectively.
A substantial body of research has demonstrated a clear correlation between elevated mortality and morbidity rates and exposure to high temperatures. In addition to its impact on physical health, hot weather can also have a detrimental effect on mental wellbeing, potentially increasing the risk of suicide.
Research
- Invite older people in the neighbourhoods to complete questionnaires about their awareness of hot weather and its health effects on them.
- Engaging the elderly and local stakeholders in focus group discussions to gain a deeper understanding of the impact of hot weather on the elderly and the provision of summer cooling facilities in the community.
- Collecting temperature and humidity data from different locations in the community and integrating them into a heat map, which indicates the cool locations in the community and the community facilities that can be used to cool off.
- Organising academic seminars to share experiences and ways to cope with hot weather with experts.
- Publications
Education
To work with government departments and local organisations in the production of educational materials, including talks, videos and pamphlets, as well as research seminars and media interviews, with the objective of raising awareness of the health risks associated with hot weather and ways to cope with the heat.
Projects
List of Publications
| Title | Author(s) | Issue Date |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme Hot Weather Events and Risk of Hospitalization for Cardiovascular and Respiratory Diseases in Older People in Hong Kong in 2012–2018 | Lai, E. T., Ho, I. Y., Ho, H. C., Chau, P. H., Yip, T. C., Wong, G. L., & Woo, J. | 2025 |
| The role of older adult-focused social vulnerability on the relationship between temperature and emergency department attendance in a subtropical Asian city | Ho JYE, Lai ETC, Chau PH, Chong KC, Woo J. | 2024 |
| The Environment and Health Inequalities in Hong Kong | CUHK Institute of Health Equity | 2024 |
| Perception of extreme hot weather and the corresponding adaptations among older adults and service providers–A qualitative study in Hong Kong | Lai, E. T. C., Chau, P. H., Cheung, K., Kwan, M., Lau, K., & Woo, J. | 2023 |
| Assessing spatial variability of extreme hot weather conditions in Hong Kong: A land use regression approach | Shi, Y., Ren, C., Cai, M., Lau, K. K. L., Lee, T. C., & Wong, W. K. | 2019 |
| Neighbouring green space and all-cause mortality in elderly people in Hong Kong: a retrospective cohort study | Wang, D., Lau, K. K. L., Ruby, H. Y., Wong, S. Y., Kwok, T. C., & Woo, J. | 2016 |






